Voltage
What is voltage?
Voltage, also known as electrical potential difference, is a measure of the electric potential energy per unit charge in an electrical circuit. It is expressed in volts (V) and is the force that drives electric current through a circuit. Simply put, voltage is the difference in electric potential between two points in a circuit and is responsible for producing an electric current when a circuit is closed.
Example of voltage in a simple direct current (dc) circuit:
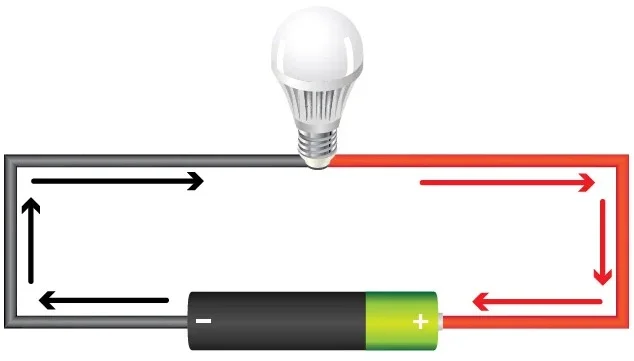
Voltage is either alternating current (ac) voltage or direct current (dc) voltage. Ways they differ:
Alternating current voltage
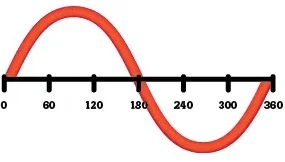
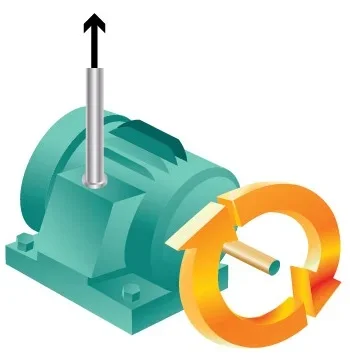
Generators convert rotating motion into electricity. The rotary motion is commonly caused by flowing water (hydroelectric power) or steam from water heated by gas, oil, coal or nuclear power.
Direct current voltage
Why measuring voltage is useful?
Measuring voltage is useful because it provides information about the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit, which can be used to determine the amount of current flowing in the circuit and the power being consumed. This information can be used to diagnose and troubleshoot electrical problems, monitor the performance of electrical systems, and control the flow of electricity in a circuit. By measuring voltage, engineers and technicians can ensure that electrical systems are functioning safely and efficiently.
What is potential difference?
Potential difference, also known as voltage, is a measure of the energy difference between two points in an electrical circuit. It is defined as the amount of energy per unit of charge that is required to move a charged particle from one point to another.
In a simple circuit, the potential difference between two points is equal to the amount of work done by an electrical force in moving a unit charge from one point to the other. This is described by the formula: V = W/Q, where V is the potential difference, W is the work done, and Q is the charge that is moved.
Potential difference is a crucial concept in electricity and electronics, as it drives the flow of electric charge through a circuit. The higher the potential difference between two points, the more energy is available to drive the flow of charge, and the larger the current will be in the circuit.
In practical applications, potential difference is often measured in volts (V), which is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta. The voltage supplied by a typical household electrical outlet is around 120V, while the voltage supplied by a car battery is usually 12V.
The Importance of Voltage Regulation in Electrical Systems
Voltage regulation is crucial in electrical systems to ensure stable and consistent power supply. It helps maintain a steady voltage level despite changes in load or supply conditions. This is important for several reasons:
Voltage regulation is an essential component of electrical systems, ensuring stable and consistent power supply, protecting equipment, improving power quality, maintaining system efficiency, and avoiding safety hazards.
Voltage Drop: Causes and Solutions
Voltage drop is a reduction in voltage level along an electrical conductor, caused by the resistance of the conductor and the load being supplied.
Causes of voltage drop
Solutions to voltage drop
AC vs DC Voltage: Differences and Applications
Differences
Applications
AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) voltages have different applications in electrical systems.
AC voltage is widely used in power transmission and distribution systems as it can be easily converted to high or low voltages and is more efficient to transmit over long distances. It is also commonly used in household appliances, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and televisions.
DC voltage, on the other hand, is used in applications where a constant voltage is needed, such as in batteries, electronic devices (e.g. computers, smartphones), and electric vehicles. It is also used as a power source in some industrial processes and in certain types of welding.
Voltage Fluctuations and Its Effects on Electronics
Voltage fluctuations refer to sudden changes in the voltage level in an electrical circuit. They can have a significant impact on electronics, leading to malfunctions or permanent damage. This is because voltage fluctuations can cause voltage spikes or dips, which can stress and damage sensitive electronic components. The effects of voltage fluctuations can range from subtle, such as reducing the lifespan of electronics, to catastrophic, such as causing immediate equipment failure or even fire. To mitigate the effects of voltage fluctuations, it is important to use voltage regulators, surge protectors, or uninterruptible power supplies to maintain a stable voltage level.
High Voltage Safety Precautions and Best Practices
High voltage electrical systems can pose significant dangers to workers and the public if proper safety precautions and best practices are not followed. Some key guidelines for working with high voltage equipment include:
By following these safety precautions and best practices, workers can minimize the risks associated with working with high voltage electrical systems and protect themselves, their colleagues, and the public from harm.
Conclusion
Voltage is a crucial aspect of electricity and a measure of the electric potential difference between two points in a circuit. It drives the flow of electric current and is a key factor in the functioning of electrical devices. Understanding voltage and its relationship with current, resistance, and power is essential for anyone working in electrical engineering or related fields. In summary, voltage plays a vital role in the functioning of our modern world and its importance cannot be overstated.













