Top 10 Anti-Inflammatory Foods You Can Eat
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection, playing a vital role in the healing process. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to various health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Fortunately, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can help combat this issue. In this blog, we will explore a range of foods known for their anti-inflammatory properties, allowing you to make informed choices for a healthier lifestyle.
Berries

Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, are rich in antioxidants called anthocyanins. These compounds have been shown to reduce inflammation and protect against oxidative stress. Incorporating berries into your diet, whether as a snack or topping for yogurt and oatmeal, can provide a flavorful and nutritious anti-inflammatory boost.
Fatty Fish

Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s have potent anti-inflammatory effects, reducing the production of inflammatory molecules like cytokines and prostaglandins. Consuming fatty fish at least twice a week can help decrease inflammation and promote heart health.
Leafy Green Vegetables

Leafy greens, including spinach, kale, and Swiss chard, are packed with nutrients and phytochemicals that possess anti-inflammatory properties. These vegetables contain high amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants like vitamin K, vitamin E, and carotenoids. Including leafy greens in salads, smoothies, or sautés can enhance your anti-inflammatory diet.
Turmeric
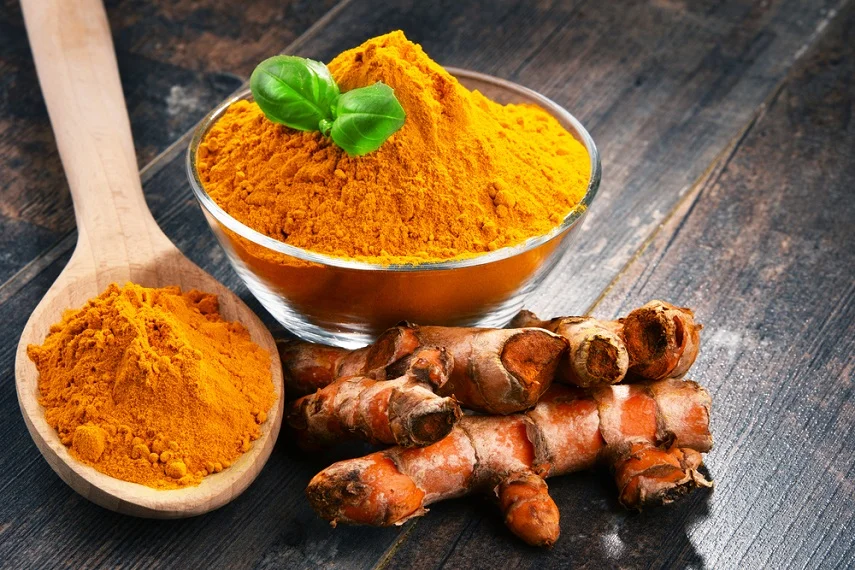

Turmeric is a vibrant yellow spice widely used in Asian cuisine. It contains a powerful compound called curcumin, renowned for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Curcumin inhibits various molecules involved in the inflammatory response, providing potential relief for conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease. Incorporating turmeric into your cooking or enjoying a cup of golden milk can help harness its anti-inflammatory benefits.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil
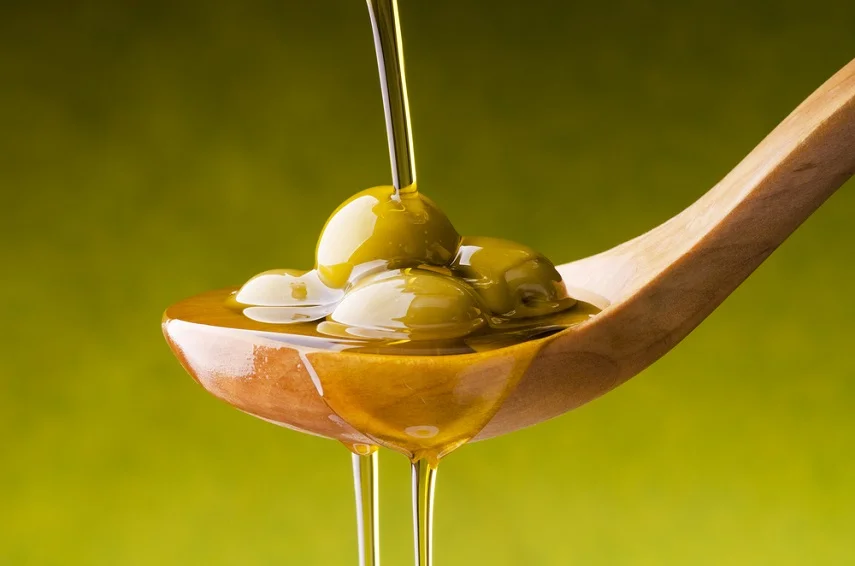

Extra virgin olive oil is a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It contains oleocanthal, a compound with similar effects to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Replacing unhealthy fats with extra virgin olive oil in cooking and salad dressings can contribute to a healthier inflammatory response.
Nuts and Seeds
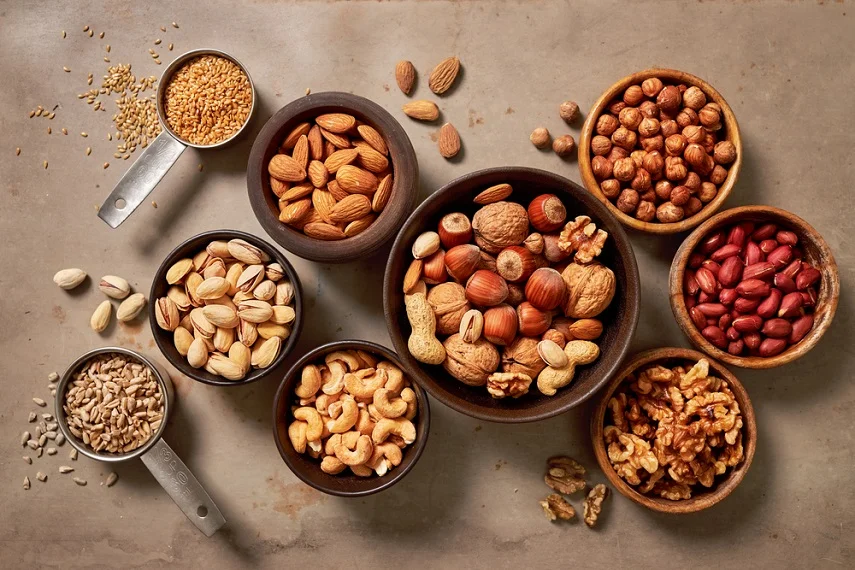

Nuts and seeds, such as almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds, are packed with beneficial nutrients, including healthy fats and antioxidants. They are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which is converted in the body into anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids. Snacking on a handful of nuts or incorporating them into your meals can help reduce inflammation and provide other health benefits.
Ginger
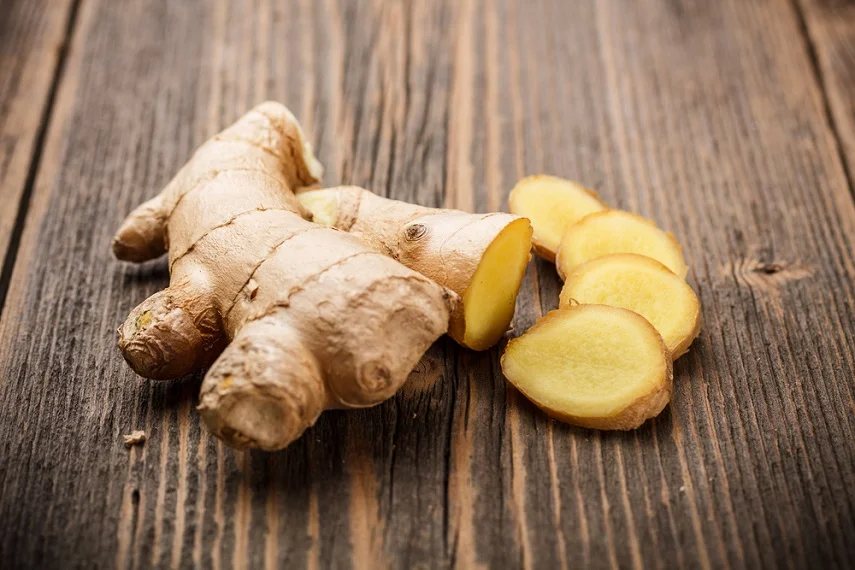

Ginger is a spice widely recognized for its culinary and medicinal uses. It contains gingerol, a bioactive compound that exhibits potent anti-inflammatory effects. Ginger has been found to alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis and reduce muscle soreness. Adding fresh ginger to your tea, stir-fries, or smoothies can infuse your meals with its anti-inflammatory goodness.
Green Tea
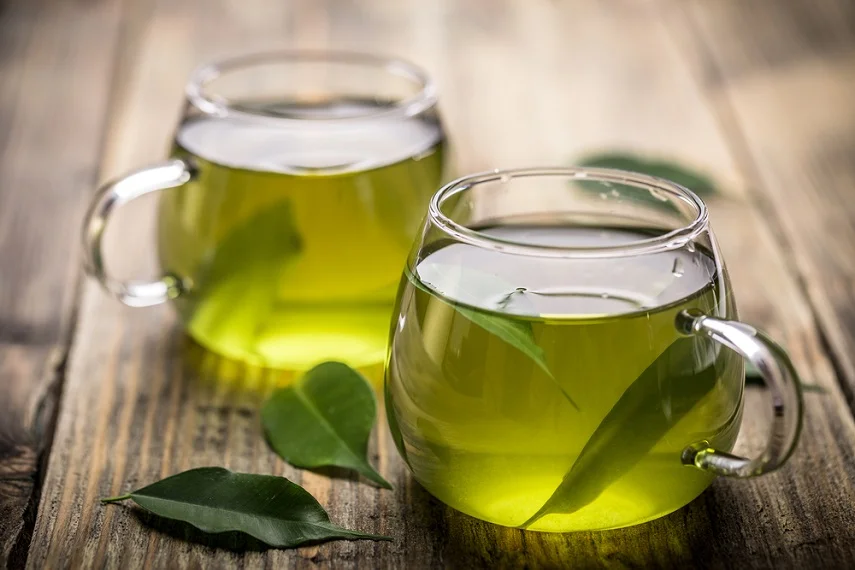

Green tea is not only a refreshing beverage but also a source of powerful antioxidants called catechins. These compounds possess anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Drinking green tea regularly may help reduce inflammation and promote overall well-being.
Garlic
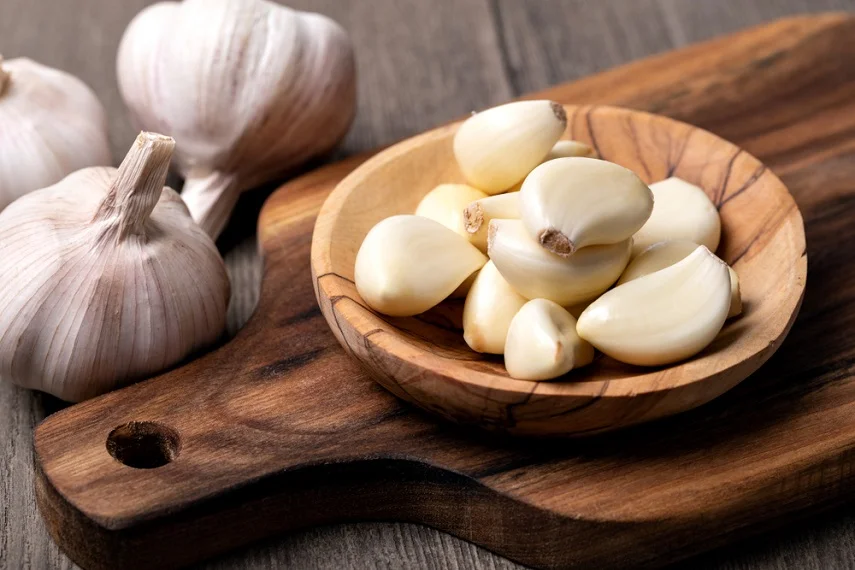

Garlic is not only a flavorful addition to numerous dishes but also possesses remarkable anti-inflammatory properties. It contains a compound called diallyl disulfide, which has been shown to inhibit inflammatory enzymes and reduce inflammation in the body. Adding fresh garlic to your cooking or incorporating it into sauces and dressings can provide both flavor and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Dark Chocolate
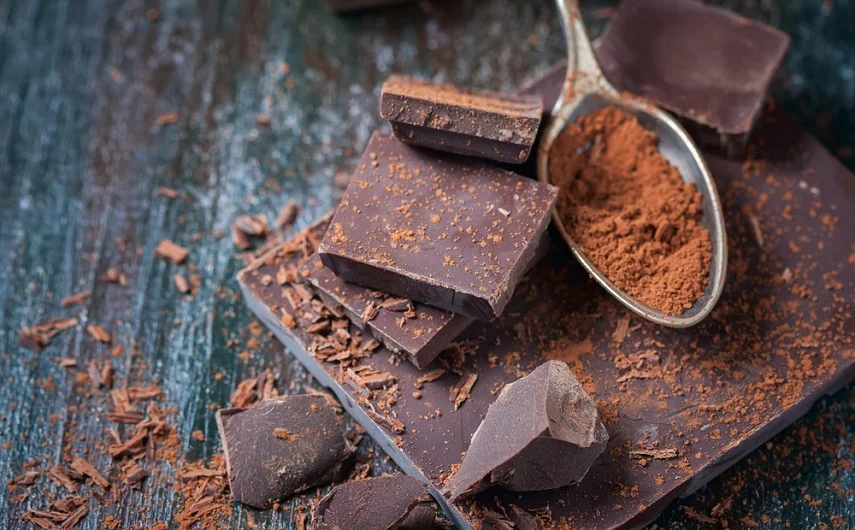

Good news for chocolate lovers! Dark chocolate with a high cocoa content (70% or more) contains flavonoids, specifically epicatechin, which has potent anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown that consuming dark chocolate can reduce markers of inflammation, improve heart health, and enhance overall well-being. However, moderation is key, as chocolate is still calorie-dense. Enjoy a small piece of dark chocolate as an occasional treat to reap its anti-inflammatory rewards.
Bottom Line
Incorporating these anti-inflammatory foods into your diet can be a proactive step toward reducing chronic inflammation and promoting better health. Remember, the key is to adopt a balanced approach, focusing on a variety of nutrient-dense foods and maintaining an overall healthy lifestyle. By making these food choices, you can take control of your well-being and enjoy the benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet.